streamtime <- 0.2 * 60 #set time out in minutes
tweets_per_state <- 5 #number of tweets per state to be analyzed.
# Section One - Setup ----
# install.packages("textdata")
# install.packages("tidytext")
# install.packages("rtweet")
# install.packages("tidyverse")
# install.packages("plotly")
# install.packages("extrafont")
# install.packages("gganimate")
# install.packages("gifski")
library(tidyverse)
library(rtweet)
library(textdata)
library(tidytext)
library(plotly)
library(extrafont)
library(gganimate)
library(gifski)
library(readxl)
# Section Two - Stream Data ----
# no upfront-parse, save as json file
filenames <- c("stream_data_unparsed_b.json", "stream_data_raw_unparsed_t.json")
q <- c("biden", "trump")
for (i in 1:2) {
stream_tweets(
q = q[i],
#is_quote = "FALSE", #could be activated for removing quotes
parse = FALSE,
timeout = streamtime,
file_name = filenames[i]
)
}
# Section Three - Collect Data (Biden) ----
data_b <- parse_stream(filenames[1]) #parse from json file
user_data_b <- users_data(data_b) #get metadata for users
# code below was used to check for the unique identifier to use, we see that both
# screen_name and user_id can be used going forward, user_id was chosen.
# length(unique(data_b$screen_name))
# length(unique(data_b$user_id))
# code below was used to check where location info was most available,
# either in "location" or "quoted_location".
# location_availability_1 <- user_data_b %>%
# select("user_id", "location")
# location_availability_2 <- data_b %>%
# select("user_id", "quoted_location")
# location_availability_1_na <- remove_missing(location_availability_1)
# location_availability_2_na <- remove_missing(location_availability_2)
# retained_location_data_1 <- count(location_availability_1_na)/count(location_availability_1) #retains ~58% for location info not equal to N/A
# retained_location_data_2 <- count(location_availability_2_na)/count(location_availability_2) #retains ~23% for location info not equal to N/A
# merge tibbles to have a unified one with all variables
user_data_b <- user_data_b %>%
distinct(user_id, .keep_all = TRUE)
data_b <- data_b %>%
distinct(user_id, .keep_all = TRUE)
data_b <- inner_join(x=user_data_b, y=data_b, by=c("user_id" = "user_id")) %>%
select("user_id", "location.x", "text", "lang") %>%
rename(location = "location.x") %>%
filter(lang %in% c("en", "und")) %>% #only tweets in english
remove_missing() #only complete observations
# Section Four - Clean Data (Biden) ----
# clean location vector
location_vector_b <- pull(data_b, location)
location_vector_b <- location_vector_b %>%
str_trim(side = "both") %>%
str_to_lower() %>%
str_squish()
data_b <- data_b %>%
mutate(location = location_vector_b) #add back the cleaned vector
# clean text vector
data_b$text <- data_b$text %>% str_to_lower()
data_b$text <- gsub("http.*", "", data_b$text) #remove any links
data_b$text <- gsub("https.*", "", data_b$text) #remove any links
data_b$text <- gsub("&", "&", data_b$text) #remove any links
data_b$text <- gsub("\\$", "", data_b$text) #remove "$" since special character in R
data_b <- data_b %>%
filter(!str_detect(text, "trump")) #filter out tweets containing trump
# Section Five - Classify Data (Biden) ----
state_ab <- str_to_lower(state.abb)
state_name <- str_to_lower(state.name)
# initiating tibble
tweet_matrix_b <- as_tibble(data.frame(matrix(nrow=as.numeric(count(data_b)),ncol=length(state_ab))))
colnames(tweet_matrix_b) <- state_ab
# creates an identification matrix, showing where data is available
for (i in 1:length(tweet_matrix_b)) {
tweet_matrix_b[i] <-
if_else(
str_detect(pull(data_b, location), state_name[i]) |
str_detect(pull(data_b, location), state_ab[i])
== TRUE,
"y",
"n"
)
}
# uses the identification matrix as a key to build a matrix of tweets
for (j in 1:length(tweet_matrix_b)) {
for (i in 1:as.numeric(count(tweet_matrix_b))) {
tweet_matrix_b[i,j] <-
if_else(
as.character(tweet_matrix_b[i,j])
== "y",
as.character(data_b[i,3]), #the "3" will have to be changed if more variables are selected in creation of "data_b"
"null"
)
}
}
# the code below can be used to check the number of observations actually collected for the candidate, but is not essential.
# biden_observations <- as_tibble(data.frame(matrix(nrow=1,ncol=length(state_ab)))) #initiating tbl for number of observations.
# colnames(biden_observations) <- state_ab
#
# # this loop counts the number of observations for biden for each us state and puts them into a matrix.
# for (i in 1:50) {biden_observations[,i] <-
# as.numeric(count(local_var <- tweet_matrix_b %>%
# filter(tweet_matrix_b[,i] != "null")))
# }
# biden_observations
# Section Six - Find Sentiment in Data (Biden) ----
# adjusting bing lexicon
bing_lex <- get_sentiments("bing") %>%
filter(word != "trump")
# initiating matrices for tokens and sentiment
sentiment_b <- as_tibble(data.frame(matrix(nrow=1,ncol=length(state_ab))))
sentiment_b[,1:50] <- 0
colnames(sentiment_b) <- state_ab
column_local <- tibble()
tokens_local <- tibble()
# extract tokens & evaluate sentiment
time_before <- Sys.time() #this loop tends to be time consuming for large amounts of tweets
for (j in 1:50) {
column_local <- tweet_matrix_b[,j] #column_local is used to select each individual us state from the tweet matrix.
colnames(column_local) <- "column_name"
column_local <- filter(column_local, column_name != "null") #remove "null" rows.
if(as.integer(count(column_local)) < tweets_per_state){
while (as.integer(count(column_local)) < tweets_per_state) { #this is for redundancy, if the streamtime is short each state might not get enough tweets for sentiment analysis.
column_local <- add_row(column_local, column_name = "notaword")
}
}
for (i in 1:tweets_per_state) {
tokens_local <- column_local[i,1] #tokens_local is used to extract the tokens of each individual tweet for each us state.
colnames(tokens_local) <- "column_name"
tokens_local <- unnest_tokens(tokens_local, word, "column_name")
tokens_local <- inner_join(x = tokens_local, y= bing_lex, by = "word") #this is the matching with the "bing" lexicon.
tokens_local <- tokens_local %>%
count(sentiment) %>%
spread(sentiment, n, fill = 0)
if(count(tokens_local) == 0){ #the following if statements are to ensure that each tokens_local has the correct columns.
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, negative = 0, positive = 0); #if sentiment is missing it is set to zero.
tokens_local <- add_row(tokens_local, negative = 0, positive = 0)
}
if(!exists("negative", tokens_local)){
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, negative = 0)
}
if(!exists("positive", tokens_local)){
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, positive = 0)
}
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, sentiment = positive - negative) #sentiment is positive-negative.
if(tokens_local$sentiment > 0){ #normalize each user's sentiment to ± 1
tokens_local$sentiment = 1
}
if(tokens_local$sentiment < 0){ #normalize each user's sentiment to ± 1
tokens_local$sentiment = -1
}
sentiment_b[i,j] <- tokens_local$sentiment #this is the final matrix with individual sentiment.
}
}
time_after <- Sys.time()
time_elapsed <- time_after - time_before
time_elapsed
# Section Seven - Collect Data (Trump) ----
data_t <- parse_stream(filenames[2]) #parse from json file
user_data_t <- users_data(data_t) #get metadata for users
# merge tibbles to have a unified one with all variables
user_data_t <- user_data_t %>%
distinct(user_id, .keep_all = TRUE)
data_t <- data_t %>%
distinct(user_id, .keep_all = TRUE)
data_t <- inner_join(x=user_data_t, y=data_t, by=c("user_id" = "user_id")) %>%
select("user_id", "location.x", "text", "lang") %>% #possible extensions, "created_at", "name.x"
rename(location = "location.x") %>%
filter(lang %in% c("en", "und")) %>% #only tweets in english
remove_missing() #only complete observations
# Section Eight - Clean Data (Trump) ----
# clean location vector
location_vector_t <- pull(data_t, location)
location_vector_t <- location_vector_t %>%
str_trim(side = "both") %>%
str_to_lower() %>%
str_squish()
data_t <- data_t %>%
mutate(location = location_vector_t) #add back the cleaned vector
# clean text vector
data_t$text <- data_t$text %>% str_to_lower()
data_t$text <- gsub("http.*", "", data_t$text) #remove any links
data_t$text <- gsub("https.*", "", data_t$text) #remove any links
data_t$text <- gsub("&", "&", data_t$text) #remove any links
data_t$text <- gsub("\\$", "", data_t$text) #remove "$" since special character in R
data_t <- data_t %>%
filter(!str_detect(text, "biden")) #filter out tweets containing biden
# Section Nine - Classify Data (Trump) ----
# categorization of tweets into US States
# initiating tibble
tweet_matrix_t <- as_tibble(data.frame(matrix(nrow=as.numeric(count(data_t)),ncol=length(state_ab))))
colnames(tweet_matrix_t) <- state_ab
# creates an identification matrix, showing where data is available
for (i in 1:length(tweet_matrix_t)) {
tweet_matrix_t[i] <-
if_else(
str_detect(pull(data_t, location), state_name[i]) |
str_detect(pull(data_t, location), state_ab[i])
== TRUE,
"y",
"n"
)
}
# uses the identification matrix as a key to build a matrix of tweets
for (j in 1:length(tweet_matrix_t)) {
for (i in 1:as.numeric(count(tweet_matrix_t))) {
tweet_matrix_t[i,j] <-
if_else(
as.character(tweet_matrix_t[i,j])
== "y",
as.character(data_t[i,3]), #the "3" will have to be changed if more variables are selected in creation of "data_b"
"null"
)
}
}
# the code below can be used to check the number of observations actually collected for the candidate, but is not essential.
# trump_observations <- as_tibble(data.frame(matrix(nrow=1,ncol=length(state_ab)))) #initiating tbl for number of observations.
# colnames(trump_observations) <- state_ab
#
# # this loop counts the number of observations for trump for each us state and puts them into a matrix.
# for (i in 1:50) {
# trump_observations[,i] <-
# as.numeric(count(local_var <- tweet_matrix_t %>%
# filter(tweet_matrix_t[,i] != "null")))
# }
# trump_observations
# Section Ten - Find Sentiment in Data (Trump) ----
# adjusting bing lexicon
bing_lex <- get_sentiments("bing") %>%
filter(word != "trump")
# initiating matrices for tokens and sentiment
sentiment_t <- as_tibble(data.frame(matrix(nrow=1,ncol=length(state_ab))))
sentiment_t[,1:50] <- 0
colnames(sentiment_t) <- state_ab
column_local <- tibble()
tokens_local <- tibble()
# extract tokens & evaluate sentiment
time_before <- Sys.time() #this loop tends to be time consuming for large amounts of tweets
for (j in 1:50) {
column_local <- tweet_matrix_t[,j] #column_local is used to select each individual us state from the tweet matrix.
colnames(column_local) <- "column_name"
column_local <- filter(column_local, column_name != "null") #remove "null" rows.
if(as.integer(count(column_local)) < tweets_per_state){
while (as.integer(count(column_local)) < tweets_per_state) { #this is for redundancy, if the streamtime is short each state might not get enough tweets for sentiment analysis.
column_local <- add_row(column_local, column_name = "notaword")
}
}
for (i in 1:tweets_per_state) {
tokens_local <- column_local[i,1] #tokens_local is used to extract the tokens of each individual tweet for each us state.
colnames(tokens_local) <- "column_name"
tokens_local <- unnest_tokens(tokens_local, word, "column_name")
tokens_local <- inner_join(x = tokens_local, y= bing_lex, by = "word") #this is the matching with the "bing" lexicon.
tokens_local <- tokens_local %>%
count(sentiment) %>%
spread(sentiment, n, fill = 0)
if(count(tokens_local) == 0){ #the following if statements are to ensure that each tokens_local has the correct columns.
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, negative = 0, positive = 0); #if sentiment is missing it is set to zero.
tokens_local <- add_row(tokens_local, negative = 0, positive = 0)
}
if(!exists("negative", tokens_local)){
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, negative = 0)
}
if(!exists("positive", tokens_local)){
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, positive = 0)
}
tokens_local <- mutate(tokens_local, sentiment = positive - negative) #sentiment is positive-negative.
if(tokens_local$sentiment > 0){ #normalize each user's sentiment to ± 1
tokens_local$sentiment = 1
}
if(tokens_local$sentiment < 0){ #normalize each user's sentiment to ± 1
tokens_local$sentiment = -1
}
sentiment_t[i,j] <- tokens_local$sentiment #this is the final matrix with individual sentiment.
}
}
time_after <- Sys.time()
time_elapsed <- time_after - time_before
time_elapsed
# Section Eleven - Aggregate Sentiments ----
sentiment <- sentiment_b*0 #initiating matrix for sentiment
# this loop aggregates the sentiments of both candidates.
# from before, the sentiment of each tweet has been normalized to ±1.
for (j in 1:50) {
for (i in 1:as.numeric(count(sentiment_b))) {
sentiment[i,j] <- sentiment[i,j] + sentiment_t[i,j] - sentiment_b[i,j]
sentiment[i+1,j] <- sentiment[i,j]
}
}
sentiment <- sentiment[-as.numeric(count(sentiment)),] #remove last duplicate row
sentiment <- sentiment %>%
mutate(tweet_count = 1:as.numeric(count(sentiment))) %>%
pivot_longer(state_ab[], names_to = "state") %>%
rename(Sentiment = "value") %>%
mutate(tooltip = paste0(str_to_title(state_name), "\n", Sentiment))
sentiment$state <- sentiment$state %>%
str_to_upper()
# Section Twelve - Gradient Map ----
fontstyle = list(
family = "Space Mono",
size = 10,
color = "black"
)
label = list(
bgcolor = "#FFFFFF",
bordercolor = "transparent",
font = fontstyle
)
us_graph = plot_geo(sentiment,
locationmode = "USA-states",
frame = ~tweet_count) %>% #set the bottom slider for the map.
add_trace(locations = ~state,
z = ~Sentiment,
zmin = min(sentiment$Sentiment),
zmax = -min(sentiment$Sentiment),
color = ~Sentiment,
colorscale = "RdBu", #alternative: Bluered, RdBu
text = ~tooltip,
hoverinfo = "text") %>%
layout(geo = list(scope = "usa"),
font = list(family = "Space Mono"),
title = "U.S Electoral Outcome\n(Aggregated Tweets)") %>%
style(hoverlabel = label) %>%
colorbar(
outlinecolor = "#000000",
y = 0.8,
thickness = 25,
len = 0.5,
title = list(text = "Sentiment"))
us_graph
# Section Thirteen - Polarized Map ----
us_graph_polarized = plot_geo(sentiment,
locationmode = "USA-states",
frame = ~tweet_count) %>% #add bottom slider for map.
add_trace(locations = ~state,
z = ~Sentiment,
zmin = -1,
zmax = 1,
color = ~Sentiment,
colorscale = "RdBu", #alternative: Bluered, RdBu
text = ~tooltip,
hoverinfo = "text") %>%
layout(
geo = list(scope = "usa"),
font = list(family = "Space Mono"),
title = "U.S Electoral Outcome\n(Aggregated Tweets)") %>%
style(hoverlabel = label) %>%
colorbar(
outlinecolor = "#000000",
y = 0.8,
thickness = 25,
len = 0.5,
tickmode = "array",
tickvals = c(-0.7,0,0.7),
ticktext = c("Biden",0,"Trump"),
title = list(text = "Sentiment"))
us_graph_polarized
# Section Fourteen - Data Wrangling for Animation ----
# data is imported for number of electoral votes per state, which will be the size in the animation.
electoral_votes <- read_excel("~/Documents/UiO/Autumn 2020/Data Science.ECON4170/Project/electoral_votes.xlsx")
electoral_votes <- electoral_votes %>%
rename(state = State) %>%
mutate(region = as.character(state.region))
electoral_votes$state <- str_to_upper(state_ab)
sentiment_aggregated_b <- sentiment_b*0 # initiating matrix for aggregated biden series
sentiment_aggregated_t <- sentiment_t*0 # initiating matrix for aggregated trump series
sentiment_animation <- tibble()
# this loop is replacing the loop in section eleven.
# we now want to keep the sentiment of each of the candidate separate to see the evolution over time.
# it will be used as animation axis.
for (j in 1:50) {
for (i in 1:as.numeric(count(sentiment_b))) {
sentiment_aggregated_b[i,j] <- sentiment_aggregated_b[i,j] + sentiment_b[i,j]
sentiment_aggregated_b[i+1,j] <- sentiment_aggregated_b[i,j]
}
}
for (j in 1:50) {
for (i in 1:as.numeric(count(sentiment_t))) {
sentiment_aggregated_t[i,j] <- sentiment_aggregated_t[i,j] + sentiment_t[i,j]
sentiment_aggregated_t[i+1,j] <- sentiment_aggregated_t[i,j]
}
}
sentiment_aggregated_b <- sentiment_aggregated_b[-as.numeric(count(sentiment_aggregated_b)),] #remove last duplicate row
sentiment_aggregated_t <- sentiment_aggregated_t[-as.numeric(count(sentiment_aggregated_t)),] #remove last duplicate row
sentiment_aggregated_b <- sentiment_aggregated_b %>%
mutate(tweet_count = 1:as.numeric(count(sentiment_aggregated_b))) %>%
pivot_longer(state_ab[], names_to = "state") %>%
rename(Biden = "value")
sentiment_aggregated_t <- sentiment_aggregated_t %>%
mutate(tweet_count = 1:as.numeric(count(sentiment_aggregated_t))) %>%
pivot_longer(state_ab[], names_to = "state") %>%
rename(Trump = "value")
sentiment_aggregated_b$state <- sentiment_aggregated_b$state %>%
str_to_upper()
sentiment_aggregated_t$state <- sentiment_aggregated_t$state %>%
str_to_upper()
sentiment_animation <- sentiment_aggregated_b %>%
mutate(Trump = sentiment_aggregated_t$Trump)
sentiment_animation <- left_join(
x = sentiment_animation,
y = electoral_votes,
by = "state")
# Section Fifteen - Graphing for Animation ----
candidate_graph = sentiment_animation %>%
ggplot(aes(x = Trump,
y = Biden,
color = region,
size = votes)) +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5, stroke = 0) +
xlim(min(sentiment_animation$Trump), -min(sentiment_animation$Trump)) +
ylim(min(sentiment_animation$Biden), -min(sentiment_animation$Biden)) +
scale_size_continuous(name = "Electoral Votes", range = c(3,10)) +
scale_color_brewer(name = "U.S Region", guide = "legend", palette = "Set2") +
labs(title = "Aggregated Sentiment of the 50 U.S States by Region",
x = "Trump Sentiment",
y = "Biden Sentiment") +
guides(color = guide_legend(override.aes = list(size = 5))) +
geom_vline(xintercept = 0, color = "black") +
geom_hline(yintercept = 0, color = "black") +
theme(panel.grid.minor = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major = element_blank(),
legend.position = "bottom",
legend.box = "vertical",
legend.margin = margin(),
legend.title = element_text(size = 8),
legend.text = element_text(size = 8),
plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5),
plot.background = element_rect(fill = "#FFFFFF"),
panel.background = element_rect(fill = "#FFFFFF"),
legend.background = element_rect(fill = "#FFFFFF"))
candidate_graph
# Section Sixteen - Animation ----
candidate_graph_anim <- candidate_graph +
transition_time(tweet_count) +
labs(subtitle = "Number of Tweets: {frame_time}") +
shadow_wake(wake_length = 0.1)
animate(candidate_graph_anim, height = 500, width = 800, fps = 30,
duration = 10, end_pause = 60, res = 100)
# optional for saving the rendered animation as a .gif file.
# anim_save("candidate_sentiment.gif")
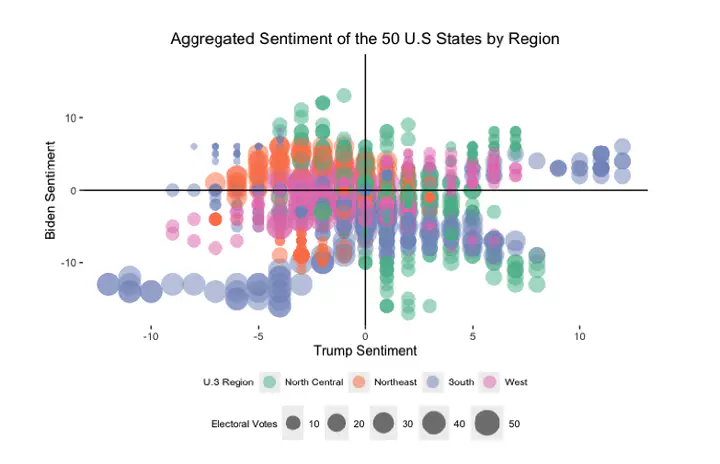 Twitter sentiment, separated by region and candidate.
Twitter sentiment, separated by region and candidate.